Concussion Care & Management
Concussions are usually associated with football, soccer and other contact sports. They can also occur during vehicle accidents, falls, and other everyday tasks. Consult a doctor immediately if you experience symptoms of a concussion.
A concussion is a traumatic brain injury caused by impact to the head or neck. This can occur during sports, a fall, or another injury. The impact traumatizes the brain. Experiencing a concussion doesn’t always result in loss of consciousness. Concussion may occur without obvious symptoms such as dizziness, memory loss, or nausea and vomiting.
The brain is more susceptible to damage after a concussion, so it’s important to avoid activities that may cause further impact to the head. Because of severe health reasons, concussion care and management should be a top priority of athletic trainers, parents, and individuals experiencing a concussion.
VSMD Approach to Concussion Care & Management
In-office evaluation to include a comprehensive history and physical exam
Computer based concussion testing (CNS Vital Signs web based testing)
Concussion Treatment Plan
Monitored recovery through follow-up visits
Individualized “Return-to-Play” plan

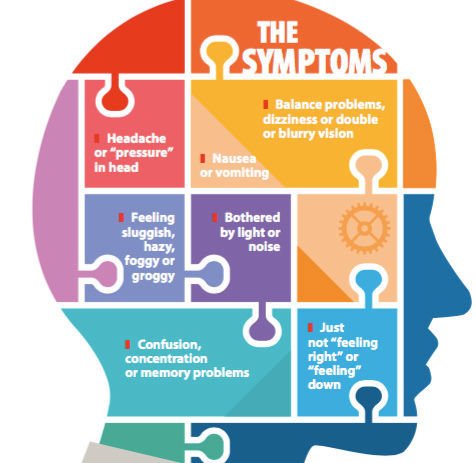
Concussion Injury - Signs to Look for
Concussion Symptoms
Headache
Fatigue or drowsiness
Confusion or fogginess
Dizziness or “seeing stars”
Amnesia surrounding the traumatic event
Nausea, vomiting
Ringing in the ears, blurry vision
A Witness May Observe
Temporary loss of consciousness
Slurred speech
Delayed response to questions
Dazed appearance
Forgetfulness, such as repeatedly asking the same questions
Fatigue or drowsiness
Symptoms after few days
Concentration and memory impairments
Irritability or other personality changes
Sensitivity to light and noise
Sleep disturbances
Psychological adjustment problems and depression
Altered taste or smell
Concussion Details
Concussion is a brain injury that is common in many sports (contact and collision sports with the highest numbers), motor vehicle accidents, and trauma (such as from falls or being hit in the head). In sports, football, wrestling, hockey, and soccer have the highest risk of concussion. A concussion occurs due to direct impact of the head or through an indirect force that affects the head and neck. A concussion is like a brain bruise. The size of the injury and the symptoms produced from injury depend on the degree and location of impact. However, the strength of the force causing concussion does not always equal the severity of symptoms. For example, an athlete who is shoved from behind may sustain a concussion and have many symptoms while an athlete who has direct head impact with another player may have only minor symptoms of concussion.
Symptoms of concussion may be very subtle or severe. They may include headache, dizziness, nausea, irritability and difficulty concentrating, balance issues, vision issues, or sleep disturbances. Activities such as school work, reading, watching TV, driving, or exercising can make symptoms worse.
If there is a concern for concussion, then an evaluation is necessary.
The doctor will determine the severity of injury.
In sports, the common question is… “When can I return to play?” The doctor will work closely with the athlete (or non-athlete) to determine a safe return to play and activity plan.
This plan is different for everyone. It may be as short as a few days or take many weeks.
The important thing to remember is that your health, especially your brain health, needs to be the priority in your treatment plan.